Even with the sharp oil price decline—a net positive for global growth—the world economic outlook is still subdued, weighed down by underlying weakness elsewhere, says the IMF’s latest WEO Update.
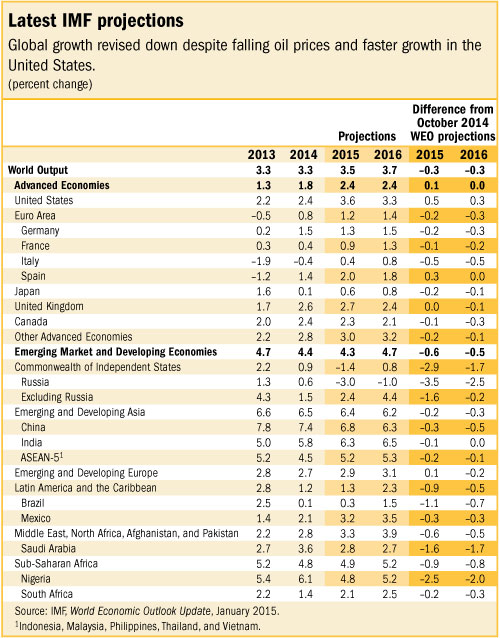
Global growth is forecast to rise moderately in 2015–16, from 3.3% in 2014 to 3.5% in 2015 and 3.7% in 2016 (see table), revised down by 0.3% for both years relative to the October 2014 World Economic Outlook (WEO).
Recent developments, affecting different countries in different ways, have shaped the global economy since the release of the October WEO, the report says. New factors supporting growth—lower oil prices, but also depreciation of euro and yen—are more than offset by persistent negative forces, including the lingering legacies of the crisis and lower potential growth in many countries.
“At the country level, the cross currents make for a complicated picture,” says Olivier Blanchard, IMF Economic Counsellor and Director of Research. “It means good news for oil importers, bad news for oil exporters. Good news for commodity importers, bad news for exporters. Continuing struggles for the countries which show scars of the crisis, and not so for others. Good news for countries more linked to the euro and the yen, bad news for those more linked to the dollar.”
Cross currents in global economy
In advanced economies, growth is projected to rise to 2.4% in both 2015 and 2016. Within this broadly unchanged outlook, however, is the increasing divergence between the United States, on the one hand, and the euro area and Japan, on the other.
For 2015, the U.S. economic growth has been revised up to 3.6%, largely due to more robust private domestic demand. Cheaper oil is boosting real incomes and consumer sentiment, and there is continued support from accommodative monetary policy, despite the projected gradual rise in interest rates. In contrast, weaker investment prospects weigh on the euro area growth outlook, which has been revised down to 1.2%, despite the support from lower oil prices, further monetary policy easing, a more neutral fiscal policy stance, and the recent euro depreciation. In Japan, where the economy fell into technical recession in the third quarter of 2014, growth has been revised down to 0.6%. Policy responses, together with the oil price boost and yen depreciation, are expected to strengthen growth in 2015–16.
In emerging market and developing economies, growth is projected to remain broadly stable at 4.3% in 2015 and to increase to 4.7% in 2016—a weaker pace than forecast in the October 2014 WEO. Three main factors explain this downward shift.
• First, the growth forecast for China, where investment growth has slowed and is expected to moderate further, has been marked down to below 7%. The authorities are now expected to put greater weight on reducing vulnerabilities from recent rapid credit and investment growth and hence the forecast assumes less of a policy response to the underlying moderation. This lower growth, however, is affecting the rest of Asia.
• Second, Russia’s economic outlook is much weaker, with growth forecast downgraded to negative 3.0% for 2015, as a result of the economic impact of sharply lower oil prices and increased geopolitical tensions.
• Third, in many emerging and developing economies, the projected rebound in growth for commodity exporters is weaker or delayed compared with the October 2014 WEO projections, as the impact of lower oil and other commodity prices on the terms of trade and real incomes is taking a heavier toll on medium-term growth. For many oil importers, the boost from lower oil prices is less than in advanced economies, as more of the related windfall gains accrue to governments (for example, in the form of lower energy subsidies).
Risks to recovery
The distribution of risks to global growth is more balanced than in October, notes the WEO Update. On the upside, lower oil prices could provide a greater boost than assumed. Other risks that could adversely affect the outlook involve the possible shifts in sentiment and volatility in global financial markets, especially in emerging market economies. The exposure to these risks, however, has shifted among emerging market economies with the sharp fall in oil prices. It has risen in oil exporters, where external and balance sheet vulnerabilities have increased, while it has declined in oil importers, for whom the windfall has provided increased buffers.
Policy priorities
The weaker global growth forecast for 2015–16 underscores the need to raise actual and potential growth in most economies, emphasizes the WEO Update. This means a decisive push for structural reforms in all countries, even as macroeconomic policy priorities differ.
In most advanced economies, the boost to demand from lower oil prices is welcome. It will also lower inflation, however, which may contribute to a further decline in inflation expectations, increasing the risk of deflation. Monetary policy must then stay accommodative to prevent real interest rates from rising, including through other means if policy rates cannot be reduced further. In some economies, there is a strong case for increasing infrastructure investment.
In many emerging market economies, macroeconomic policy space to support growth remains limited. But lower oil prices can alleviate inflation pressure and external vulnerabilities, giving room to central banks to delay raising policy interest rates.
Oil exporters, for which oil receipts typically contribute a sizable share of fiscal revenues, are experiencing larger shocks in proportion to their economies. Those that have accumulated substantial funds from past higher prices can let fiscal deficits increase and draw on these funds to allow for a more gradual adjustment of public spending to the lower prices. Others can resort to allowing substantial exchange rate depreciation to cushion the impact of the shock on their economies.
Lower oil prices also offer an opportunity to reform energy subsidies and taxes in both oil exporters and importers. In oil importers, the saving from the removal of general energy subsidies should be used toward more targeted transfers to protect the poor, lower budget deficits where relevant, and increase public infrastructure if conditions are right.